Operator Overloading (Example)
Example code:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class student{
int a;
int b;
string name;
public:
student(){
a=0;
b=0;
name="No name.";
}
student(int a,int b,string name){
this->a=a;
this->b=b;
this->name=name;
}
void print(){
cout<<"a = "<<a<<endl;
cout<<"b = "<<b<<endl;
cout<<"Name = "<<name<<endl;
}
student operator +(student ob);
};
student student::operator +(student ob){
ob.a=a+ob.a;
ob.b=b+ob.b;
name=name+" ";
ob.name=name+ob.name;
return ob;
}
int main(){
student ob1(1,40,"Hasibul"),ob2(2,33,"Hassan"),ob3;
ob1.print();
ob2.print();
ob3=ob1+ob2;
ob3.print();
return 0;
}
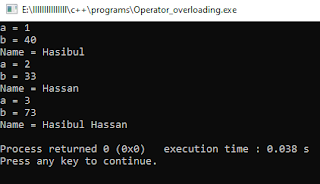
Output:
I. We never create new operator.
ii. Some of them we can not use.
` 1) "." Dote operator.
2) ".*" Direct Pointer.
3) "()?:" Terinary operator.
4) "::" Scope Resolution.
5) "sizeof".
6) "#" Preprocessor..
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class student{
int a;
int b;
string name;
public:
student(){
a=0;
b=0;
name="No name.";
}
student(int a,int b,string name){
this->a=a;
this->b=b;
this->name=name;
}
void print(){
cout<<"a = "<<a<<endl;
cout<<"b = "<<b<<endl;
cout<<"Name = "<<name<<endl;
}
student operator +(student ob);
};
student student::operator +(student ob){
ob.a=a+ob.a;
ob.b=b+ob.b;
name=name+" ";
ob.name=name+ob.name;
return ob;
}
int main(){
student ob1(1,40,"Hasibul"),ob2(2,33,"Hassan"),ob3;
ob1.print();
ob2.print();
ob3=ob1+ob2;
ob3.print();
return 0;
}
Output:
Limitation of overloading:
ii. Some of them we can not use.
` 1) "." Dote operator.
2) ".*" Direct Pointer.
3) "()?:" Terinary operator.
4) "::" Scope Resolution.
5) "sizeof".
6) "#" Preprocessor..
মন্তব্যসমূহ
একটি মন্তব্য পোস্ট করুন